(2) Leading angle and auxiliary declination: When cutting high manganese steel, the main declination should be smaller, which can increase the heat dissipation area and the tip strength of the tool, and the secondary declination should not be too large. The selection of carbide cutting tools, and generally κ r = 25 ° ~ 45 ° , κ 'r = 10 ° ~ 20 °. When the rigidity of the process system is good, take a small value, and vice versa, increase the lead angle and the off-angle. When using ceramic tools, the main declination can be larger, generally κ r = 45 ° ~ 60 °, κ r = 60 ° ~ 90 °.
(3) Blade inclination: In order to maintain the strength of the tip portion, the negative edge inclination should generally be selected when cutting high manganese steel. When using a carbide tool, λ s = -5 ° to 0 °; when using a ceramic tool, λ s = -10 ° to -5 °.
(4) Tool nose arc radius: When cutting high manganese steel, no matter which tool material is used, the tool tip part should be ground to a larger arc radius to enhance the tool tip strength and improve tool durability. Generally, r ε =1 ~ 2 mm for roughing, r ε =0.5 ~ 1 mm for semi-finishing, and r ε =0.2 to 0.5 mm for finishing . When the rigidity of the process system is good, take a large value, and vice versa.
(5) Edge chamfering: In order to ensure that the cutting edge has sufficient strength to reduce the chipping phenomenon, the cutting edge should generally be ground to a negative chamfer. Carbide cutter chamfer width b γ 1 =0.2 ~ 0.8 mm , chamfering rake angle γ 01 =-10 ° ~ -5 °; if using ceramic cutter, b γ 1 =0.2 mm , γ 01 =-20 °.
6. How to choose the cutting amount when cutting high manganese steel?
High manganese steel has poor machinability, and the cutting speed should be lower in order to maintain a certain tool durability. When using hard alloy tools, Vc = 20 ~ 40 m / min , of which the lower speed is used for roughing and the higher speed is used for semi-finishing and finishing. When using ceramic tools, you can choose a higher cutting speed, generally Vc = 50 ~ 80 m / min ( such as with Si3N4 ceramic tools, Vc ≤ 60 m / min) .
In the process of cutting high manganese steel, due to the influence of plastic deformation and cutting force, severe hardening occurs in a certain depth range under the cutting layer and the surface layer. In order to avoid the hardened layer caused by the surface of the blank and the previous pass, a larger depth of cut and feed should be selected. Generally, when roughing, α p = 3 ~ 6 mm , f = 0.3 ~ 0.8 mm / r ; α p = 6 ~ 10 mm for large rough car ; α p = 1 ~ 3 mm for semi-finished car ; f = 0.2 ~ 0.4 mm / r ; fine car hour. ≤ 1 mm ; f ≤ 0.2mm/r .
7. What are the characteristics of drilling high manganese steel carbide drills?
ZGMn13 high manganese steel is often used in the manufacture of construction machinery, mining machinery and off-road vehicles. ZGMn13 high manganese steel has a manganese content of 11% to 14%. After being subjected to water toughening treatment, this type of steel will have a strong hardening phenomenon when subjected to severe impact pressure. The hardness can reach HB450-550 and the hardened layer depth is about 0.3 mm. . In the process of deformation of the high-manganese steel, the impact force on the surface of the steel material is consumed, and the force is transmitted to the deeper inner layer. In addition, the high thermal conductivity of high manganese steel is very low, only 1/3 to 1/4 of carbon steel, which brings great difficulty to cutting. Especially when drilling, the tool wears badly and the durability is low. Therefore, cemented carbide drills are often used for high manganese steel drilling.
The body of the drilled high manganese steel cemented carbide group is made of 40Cr, and the cutting part is YG8 or YW cemented carbide. The shape of the cutting part is similar to that of the cast iron group drill, except that the height h of the drill tip is increased to 0.08 D, and the arc radius of the arc edge is increased to 0.4 D to increase the blade tip angle of the B point and improve the tip strength. Improves heat dissipation conditions and also acts as a chip. Similarly, grind the double front angle at the outer edge and grind the negative rake angle to increase the relief angle at the outer edge to 20°, as shown in Figure 1. After the drill bit is ground, use the oil stone to carefully cut the cutting edge, and there must be no serrations.
Previous Next
Besides Slurry pumps, Shijiazhuang Naipu pump Co.,ltd also sell other pumps, such as NP-WQsubmersible sewage slurry pump, NP-IS clean water pumps, NP-QJ deep well pumps and NP-ISW End Suction Pump,etc.
WQ Submersible Sewage Slurry Pump is one subermerisble pumps,is one type horizontal pump for clean water.
Application of submersible sewage slurry pumps:

Deep well pump construction
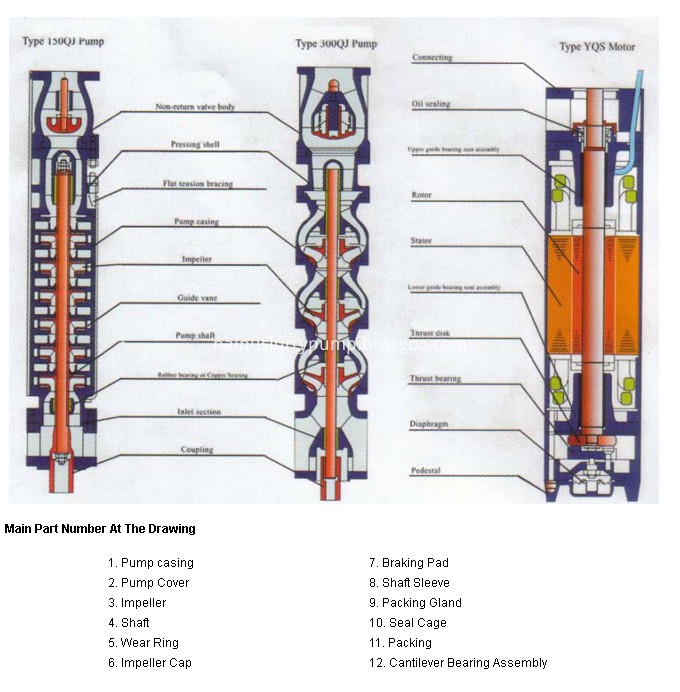
Shijiazhuang Naipu pump Co.,ltd, with more than 20 years' experiences in slurry pumps and parts, we can produce many type of pumps, welcome to contact with us.
Submersible Sewage Slurry Pump,NP-QJ Deep Well Pump,NP-ISW End Suction Pump, IS Clean Water Pump
Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com