Hydrogen energy is a very clean and renewable energy source that can be stored and transported. The use of solar energy to decompose water to produce hydrogen has become an attractive new energy technology. Inorganic semiconductor materials are currently the most widely used photocatalytic active materials. Generally, high-photocatalytic active semiconductors have a wide band gap, so that they can only absorb short-wave solar light such as ultraviolet light, and the ultraviolet light only accounts for about 5% of the full spectrum of sunlight. , resulting in the full use of solar energy difficulties. Therefore, it is very necessary to develop an organic semiconductor material capable of absorbing light in a broad spectrum and completing photocatalytic conversion. In many current schemes, a Z-type structure composed of a wide bandgap semiconductor and a narrow bandgap semiconductor is one of the effective ways to realize full spectrum photocatalysis. Recently, Prof. Xiong Yujie of the University of Science and Technology of China, based on the cation exchange synthesis route, has constructed a class of non-precious metal Z-type photocatalysts that exhibit excellent performance in broad-spectrum photolysis of water to produce hydrogen. The work was published online in the important chemical journal "Applied Chemistry in Germany" (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201700150). The co-first authors were undergraduate Yuan Qichen and doctoral student Liu Dong.
No-noble metal Z-type broad-spectrum photolysis water-hydrogen material principle diagram
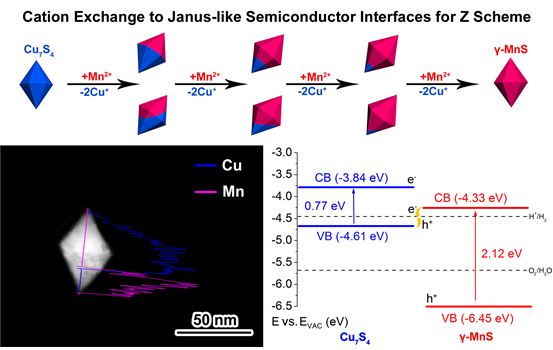
The energy conversion efficiency of a Z-type photocatalytic system mainly depends on two material structural factors: (1) a clear interface structure that determines the charge transfer efficiency between the two semiconductors; and (2) two types of sites that provide both reduction and oxidation reaction sites. The exposed surface structure of the semiconductor. In the development of Z-type photocatalytic materials in the past, the industry often introduced precious metals between the two semiconductors to improve the interface charge transfer efficiency. However, the introduction of precious metals not only increases the cost of materials, but also may have a reverse reaction at the precious metal. Therefore, it is very necessary to avoid the use of precious metals at the interface while satisfying the structural conditions of the above two materials.
Xiong Yujie's group focused on this series of challenges, using Cu7S4 nanocrystals as precursors, through the cation exchange synthesis route, and converting them into two-sided heterogeneous nanostructures constructed of Cu7S4 and g-MnS. The structure not only satisfies the requirements of the exposed surface and the clear interface structure at the same time, but also can realize the conversion from solar energy to chemical energy efficiently without using precious metals. The difference in bandgap of these two kinds of semiconductors can effectively realize complementary light absorption and exhibit improved photocatalytic hydrogen production performance under full spectrum light conditions. The research progress has opened up a new idea for the design of broad-spectrum photocatalytic materials, and it also has a catalytic effect on the design of surface interfaces of composite photocatalysts.
The work of synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy was supported by the cooperation of Prof. Zhu Junfa of the University of Science and Technology of China. The research work was supported by projects of the 973 Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the Frontier Science Key Research Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. (College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, and National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory for Collaborative Innovation in Energy and Materials Chemistry)
Grow Light For Indoor Plants 220w
Grow Light For Indoor Plants 220w, quantum board Plant Lamp 220w with 2 board, each board 350pcs led, include 3500k white+660nm red+UV+IR, samsung LM301B/LM301H quantum board with meanwell driver, meanwell driver we provide 5 yrs warranty time, normal driver 1 yr warranty.
Application:Grow Tent , indoor plants, hydroponic etc.
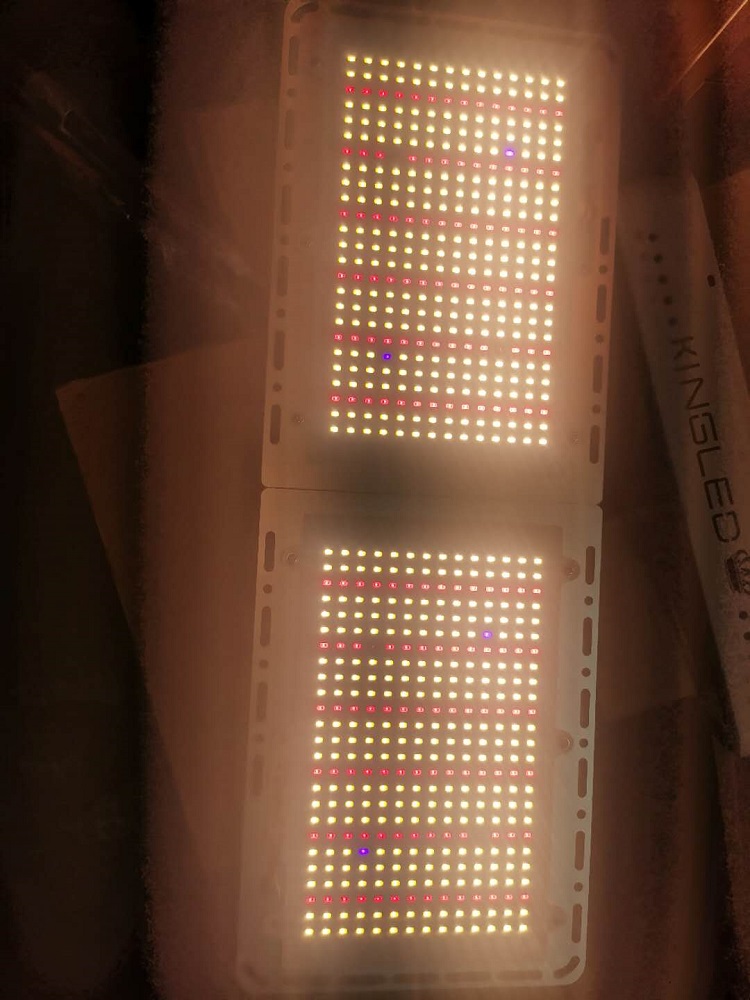



Best Lights For Indoor Growing,Led Grow Lights For Indoor Plants,Indoor Garden Light,Best Led Grow Lights For Indoor Plants
Shenzhen Wenyi Lighting Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.szwygrow.com