1. The scale of import and export has gradually expanded, and the year-on-year decline has narrowed.
In the first three quarters, the total import and export volume of the country reached US$155.8 billion, down 20.9% from the same period of the previous year. Of this total, exports were $86.7 billion, down 21.3%; imports were $711.2 billion, down 20.4%. In terms of quarterly, imports and exports in the first, second and third quarters were US$428.9 billion, US$517.9 billion and US$610.9 billion, respectively, down 24.9%, 22.1% and 16.7% respectively, of which exports were US$245.6 billion and US$276.1 billion respectively. 325 billion US dollars, down 19.8%, 23.5% and 20.5%; imports were 183.3 billion US dollars, 241.8 billion US dollars and 285.9 billion US dollars, down 30.9%, 20.4% and 11.8%. Since the third quarter, with the policy effect of stable external demand and the stabilization of international market demand, exports have exceeded 100 billion US dollars for three consecutive months, reaching 115.9 billion US dollars in September, setting a new monthly export value this year, and the year-on-year decline It was narrow to 15.2%. Driven by factors such as the expansion of domestic demand, imports reached US$103 billion in September, the first time this year that it exceeded US$100 billion, down 3.5%, and the decline was reduced to single digits for the first time. The trade surplus in the first three quarters was US$135.5 billion, down 26% year-on-year.
 2. The import price of resource products fell sharply, and the price drop had a significant impact on foreign trade.
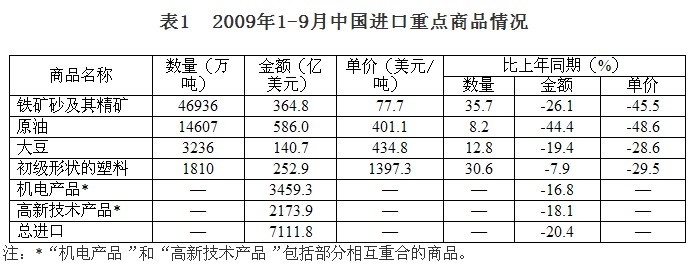
2. The import price of resource products fell sharply, and the price drop had a significant impact on foreign trade. Affected by factors such as weaker international market demand, more intense competition and continued sharp decline in commodity prices, import and export prices continued to decline year-on-year. In the first three quarters, export prices fell by 6.1% and import prices fell by 17.5%. Excluding the price factor, exports and imports fell by 16.2% and 3.5% respectively in the first three quarters. The import prices of major resource products fell more than double digits. The average price of crude oil imports fell by 48.6% in the first three quarters, iron ore fell by 45.5%, primary shape plastics fell by 29.5%, and soybeans fell by 28.6%.
3. Imports of bulk commodities continued to increase, and the decline in imports of mechanical and electrical products decreased.
In the first three quarters, the import volume of bulk energy resources maintained rapid growth, with iron ore imports increasing by 35.7%, crude oil increasing by 8.2%, primary shape plastics increasing by 30.6%, and soybeans increasing by 12.8%, but soybean imports since July. The rapid growth momentum has reversed, and imports in September fell by 33.5%. Affected by the expansion of domestic demand and the slowdown of processing trade, the import of electromechanical and high-tech products has been improving since the beginning of the year. Since the second quarter, the import of mechanical and electrical products has reached 345.9 billion US dollars, down 16.8%, and the import of high-tech products has reached 217.4 billion. The US dollar fell by 18.1%, and the decline was lower than the overall decline in imports.
 4. The decline in exports of labor-intensive products was lighter, and the decline in exports of electromechanical and high-tech products slowed down.
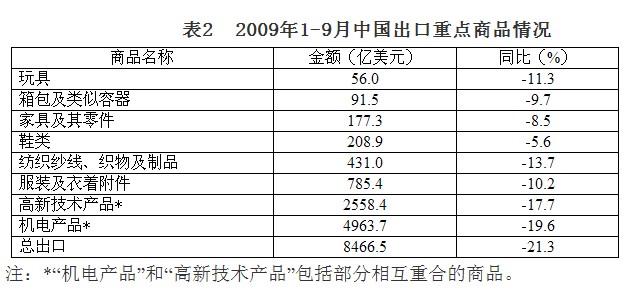
4. The decline in exports of labor-intensive products was lighter, and the decline in exports of electromechanical and high-tech products slowed down. Benefiting from the policy measures such as increasing the export tax rebate rate, coupled with relatively small elasticity of demand and obvious domestic competitive advantages, the decline in exports of labor-intensive products such as clothing is significantly lower than the overall decline in exports. In the first three quarters, apparel exports were US$78.5 billion, down 10.2%; textile exports were US$43.1 billion, down 13.7%; footwear exports were US$20.9 billion, down 5.6%; furniture exports were US$17.7 billion, down 8.5%; luggage exports were US$9.2 billion. , a decline of 9.7%; toy exports of 5.6 billion US dollars, down 11.3%. The export of electromechanical and high-tech products declined at the beginning of the year, but as the demand in the international market stabilized, the support for export credit insurance and credit increased, and the decline gradually narrowed. In the first three quarters, the export of mechanical and electrical products was 496.4 billion US dollars, down 19.6%, and the export of high-tech products was 255.8 billion US dollars, down 17.7%. In the third quarter, it dropped by 16.9% and 11.5% respectively.
 5. The decline in processing trade has gradually narrowed, and the decline in general trade exports has expanded.
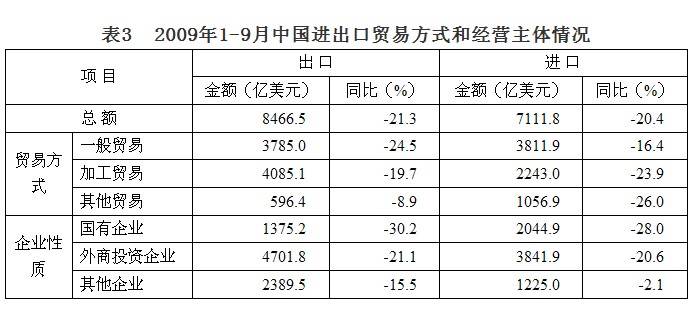
5. The decline in processing trade has gradually narrowed, and the decline in general trade exports has expanded. As the processing trade is dominated by mechanical and electrical products such as IT, the industrial chain is relatively short, and it was greatly affected in the early stage of the crisis. In the first five months of 2009, the cumulative decline in processing trade has been greater than that of general trade. Since June, as the external demand situation improved and the stable processing trade development policy gradually improved, orders have recovered, and processing trade exports have rebounded significantly. The year-on-year decline has been less than the general trade and the overall decline in exports. In the first three quarters, processing trade exports were 408.5 billion US dollars, down 19.7%, and imports were 224.3 billion US dollars, down 23.9%. Among them, processing trade exports fell 11.4% in September, and imports fell 6.9%. At the same time, the general trade exports in the first three quarters reached US$378.5 billion, down 24.5% year-on-year. The decline showed an expansion. The main reason was that the rapid growth of general trade in 2008 led to a relatively high base; imports were US$381.2 billion, down 16.4%. In September, it increased by 1.7%, and for the first time since 2009, it achieved positive growth.
6. Private enterprises are relatively less affected, and the import and export of state-owned enterprises has fallen sharply.
In recent years, Chinese private enterprises have continued to grow and develop, their operating mechanisms are flexible, their competitiveness has been further enhanced, and exports are mainly labor-intensive products, which are relatively less affected by the crisis. In the first three quarters, private enterprises exported 239 billion US dollars, down 15.5%, imports 122.5 billion US dollars, down 2.1%; foreign-invested enterprises exported 470.2 billion US dollars, down 21.1%, imports 384.2 billion US dollars, down 20.6%; state-owned enterprises exported 137.5 billion The US dollar fell 30.2%, and imports were 204.5 billion US dollars, down 28%.
 7. The decline in exports to the US and Japan has narrowed, and exports to some emerging markets have fallen sharply.
7. The decline in exports to the US and Japan has narrowed, and exports to some emerging markets have fallen sharply. Among the top 10 trading partners, the decline in exports to the United States, Japan and other countries continued to fall below the overall decline in exports. In the first three quarters, exports to the United States were $157.3 billion, down 16.9%, and exports to Japan were $69.8 billion, down 18.8%. The decline in exports to Hong Kong and ASEAN has also narrowed markedly in recent months, which is already lower than the overall decline in exports. In the first three quarters, exports to Hong Kong fell by 20.6%, and to ASEAN by 16.1%. However, the decline in exports to the EU and emerging economies such as Russia and Brazil is still relatively large, with 24.1%, 48.9% and 37.3% in the first three quarters. At the same time, imports from the EU and the United States fell by 9.2% and 12.4%, respectively, both significantly lower than the overall decline in imports. As domestic demand for resources and energy products picked up, the decline in imports from Australia and Brazil has narrowed sharply, down only 4.0% and 10.9% respectively.
 Judging from the situation in the first three quarters, under the severe situation of a sharp decline in the world economy and a severe contraction in the international market, China’s import and export scale has gradually expanded and the decline has narrowed. This achievement has not been easy. This fully shows that the Chinese government's guidelines and policies on stabilizing exports and expanding imports are correct, and the measures introduced are timely and effective.
Judging from the situation in the first three quarters, under the severe situation of a sharp decline in the world economy and a severe contraction in the international market, China’s import and export scale has gradually expanded and the decline has narrowed. This achievement has not been easy. This fully shows that the Chinese government's guidelines and policies on stabilizing exports and expanding imports are correct, and the measures introduced are timely and effective.Silica Fume For High-strength Concrete
This kind of silica fume, as a concrete additive product, can be widely used in various occasions when concrete is needed, such as adding in grout and adding in commercial concrete. Silica fume can increase the insulation and corrosion resistance of cement, and can be widely used in various railways, highways, bridges, tunnels and high-rise buildings. At the same time, the high activity and density of silica fume can also be widely used in electronic, medical, cosmetic and other industries.

silica fume for high-strength concrete, Heavy density silica fume,Highly active microsilica powder, Silica fume for grouting material,Silica ash,siliceous dust,White silica fume
Chengdu Rongjian Engineering Materials Co.Ltd , https://www.rjsilicafume.com