[China Aluminum Network] The air conditioning system consists of four major components, namely the compressor, condenser, throttling expansion mechanism and evaporator. The condenser and the evaporator are collectively referred to as heat exchangers. They are heat exchange units in refrigeration and air conditioning equipment and play a crucial role in the performance of the entire air conditioner.
With the rapid development of the air-conditioning industry, the demand for new, efficient, compact and energy-efficient heat exchangers is increasing. In particular, due to the fact that the traditional HCFC refrigerants will be replaced with fatal defects in environmental protection, and the new alternative refrigerants such as carbon dioxide work at a high pressure, the heat exchangers are required to have sufficient pressure resistance.
The multi-channel parallel flow heat exchanger has the advantages of compact structure, light weight, high heat exchange efficiency, and strong pressure resistance, and has become a more promising form of heat exchanger. As shown in Fig. 1, the parallel flow heat exchanger consists of a perforated flat tube and a corrugated louvered fin. A collector tube is provided at both ends of a porous aluminum alloy flat tube, and a spacer is partitioned within the collecting tube. Different, it is gradually decreasing trend, this variable process design makes the effective volume of the heat exchanger can be reasonably used to improve the heat transfer capacity.
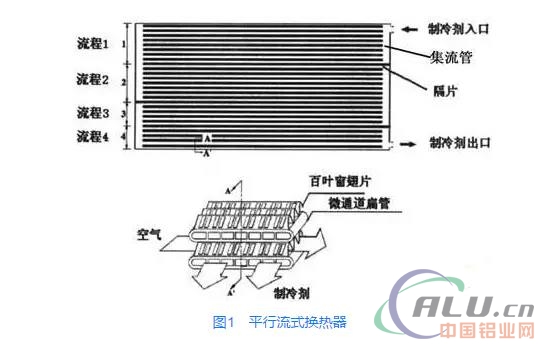
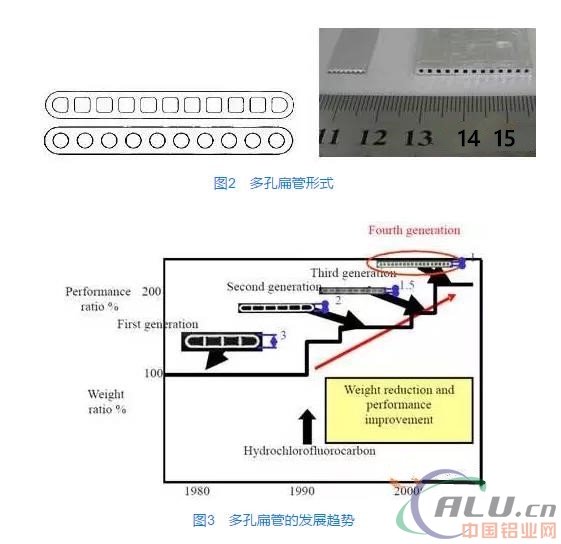
As shown in FIG. 2 , the shape of the flow path of the porous aluminum alloy flat tube is mainly rectangular and circular. Research shows that the smaller the flow channel size is, the higher the heat transfer efficiency is. When the flow channel size is less than 3 mm, the scale effect will occur in the gas-liquid two-phase flow and heat transfer in the pipe. The smaller the channel, the more obvious the size effect. In order to increase the heat transfer capacity of the heat exchanger and reduce the weight at the same time, the equivalent diameter of the flow passage of the porous flat tube is getting smaller and smaller, even to the sub-millimeter microchannel level. Figure 3 illustrates the development trend of the porous flat tube. At present, foreign countries have been able to produce the fourth-generation aluminum alloy extrusion porous flat tube with a tube thickness of 1mm and an equivalent diameter of the flow channel of 0.5mm, while our country is working hard on the fourth generation of micro Channel porous flat tube direction efforts.
2. Porous aluminum alloy flat tube extrusion process
The multi-hole flat tube for producing a parallel flow heat exchanger is obtained by an aluminum extrusion process using an aluminum alloy. In view of the structural complexity of the multi-hole flat tube, a multi-flow split mold is generally used to perform extrusion molding on the aluminum ingot blank. The split-flow combination mold can ensure uniform wall thickness, and has the advantages of simple production equipment and low production cost. FIG. 4 shows an extrusion die for manufacturing a porous flat tube, which mainly includes an extrusion cylinder, a split hole, a bypass bridge, a mold core, a working belt, and a welding chamber.

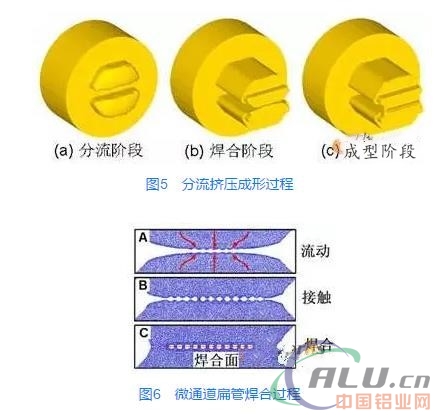
The metal flow process in the shunt die press is divided into the shunt, weld, and forming stages, as shown in Figure 5. During the shunting stage, the material is divided into two strands and enters the shunt hole; during the soldering phase, the material enters the soldering chamber and is fused together at high temperature and pressure; during the forming phase, the material fills the soldering chamber and is extruded from the working belt. The microchannel tubes have many closed sections and many welding surfaces, and the tubes are under alternating pressure conditions in the refrigeration system. Therefore, the forming quality problem of the welded surfaces becomes one of the key issues in the extrusion of multi-channel tubes. Through numerical simulation, it can be seen that the material of the entire welding process first flows into the complicated cavity formed by the welding chamber and the mandrel, and the two strands of material come into contact around the mandrel under the action of the extrusion force, due to the high temperature in the welding chamber. The effect of high pressure, two materials welded together in an extremely short time.
Split die extrusion die design is a decisive issue for the production of microchannel flat tubes. The squeeze tube can be divided into a flat die and a conical die according to the die angle of the die hole. The traditional profile extrusion is generally a flat die, that is, the die angle is 90°. This is due to the fact that the dead zone exists in the metal flow during the extrusion of the flat die, and the natural die angle formed by the metal flow is generally 40° to 70°. Therefore, the oxides and dirt on the surface of the billet are left in the dead zone. , The extrusion products produced in this way have good surface quality, but they have large extrusion pressure and high energy consumption.
The split hole is the passage of the metal flow to the welding chamber. The number, shape and shape of the split holes have a great influence on the quality of the extruded product, the extrusion force and the life of the die. The number of orifices is generally as small as possible to reduce the weld, increase the area of ​​the orifice, and reduce the extrusion force. The shape of the split hole should be as close as possible to the shape of the profile, and at the same time the strength of the die must be ensured. Therefore, the fan-shaped split hole is generally used.
The arrangement of the shunt holes is to maintain a geometric similarity with the product as far as possible, neither too close to the edge of the mold nor too close to the center of the squeeze tube. The splitter bridge is used to support the mold core, and its structure and size have a significant influence on the metal flow rate, weld quality, and mold strength. The core, also known as the tongue, is used to shape and size the stroke profile cavity. The weld chamber is the space where the split holes are divided into several pieces of metal and re-welded. The die holes are used to form the external status and dimensions of the cavity. Work belts are formed on the mold core and the die holes, and the working belt portion determines the shape and dimensional accuracy of the profiles.
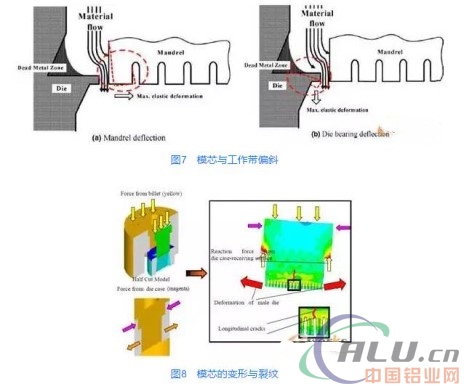
Although the traditional flat mold shunt can make the surface quality of the product good, but the extrusion force becomes very large, easy to make the core and the working belt elastic deformation and deflection, as shown in Figure 7, which will seriously affect the product than the end The shape and dimensional accuracy. What is more, if the extrusion force exceeds the tensile strength of the core material, it will cause cracks in the core, as shown in Figure 8, which affects the service life of the mold.
3 aluminum alloy heat exchanger bending process
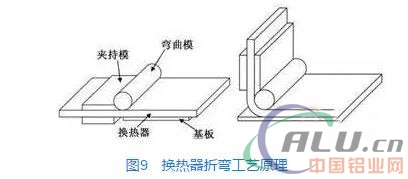
In order to ensure that the heat exchange area is constant, in order to make the air-conditioning system more compact, the brazed heat exchanger usually needs to be bent one or more times to form an "L" shape or a "G" shape. The forming process is shown in Figure 9. In general, the complete bending die includes: bending die, clamping die, and stamper (or base plate). The front end of the heat exchanger is sandwiched between the bending die and the clamping die while the trailing end is supported by the bottom plate. When bending, the clamping die is forced to rotate the entire heat exchanger around the center of the bending die and rotate at a predetermined angle as required. The bending forming process is one of the key processes of heat exchanger forming, and has an important influence on the performance of the heat exchanger.
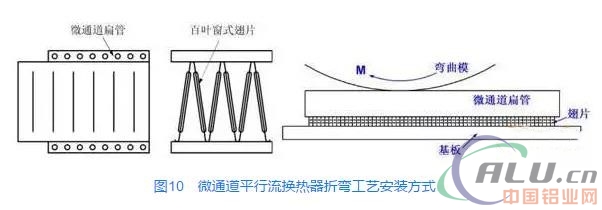
The structure and installation method of the micro-channel parallel flow heat exchangers that need to be bent are shown in Figure 10. In order to increase the convective heat transfer effect on the air side of the heat exchanger, the louvered fins brazed with the porous flat tube are wider in the width direction than the width of the flat tube. In order to prevent bending forming, the fins become unstable due to pressure contact with the mold. In the bending, the fins are aligned with the pipe, and the fins protrude out of the bend to form a cantilever structure.
After the porous flat tube is bent, the wall of the tube will be thinned, and the shape of the flow path will also be distorted. In particular, the flow area of ​​the outer flow passage of the tube after the bending is reduced more seriously. In order to ensure that the heat exchanger has sufficient pressure capacity, especially the advanced alternative working medium, the pressure of the entire air conditioning system is very high, and higher requirements are imposed on the quality of heat exchanger bending forming. The wall thickness variation and flow channel distortion were predicted by simulation methods, and the experimental results were used to verify the simulation results (Figure 11). Under high pressure conditions, the thinning rate and the flow channel distortion must be controlled to be less than 5%. By adding appropriate thrust to the heat exchanger tail, the thinning and distortion of the pipe can be effectively reduced.

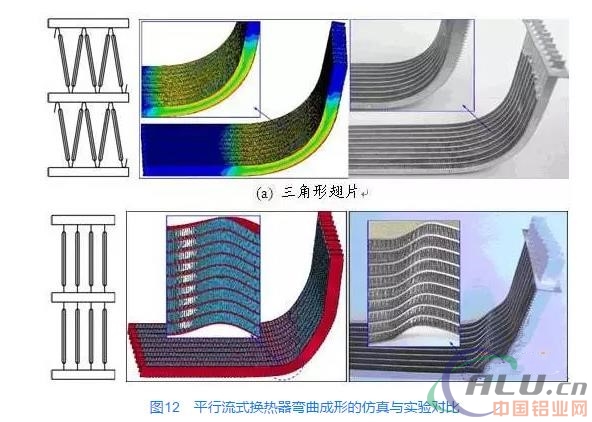
On the other hand, the overall bending is mainly forced in the plane of the flat tube. Due to the special structure of the porous flat tube itself, the thickness is relatively large, and the rigidity in the plane is greater than the stiffness perpendicular to the plane of the flat tube. Deflection buckling perpendicular to the tube plane. As shown in FIG. 12 , the simulation and experimental results show that the triangular fin heat exchanger is well-formed, and the fins are not crushing or twisting; and the rectangular fin heat exchanger may exhibit a certain degree of flexion during the forming process. phenomenon. This phenomenon shows that because of the stability of its own structure, triangular fins can enhance the stiffness perpendicular to the plane of the tube and compensate for the instability in bending. However, because of the lack of stability in the structure of the rectangular fins, the rigidity of the fins is enhanced in the vertical direction. Limited, causing instability during bending.
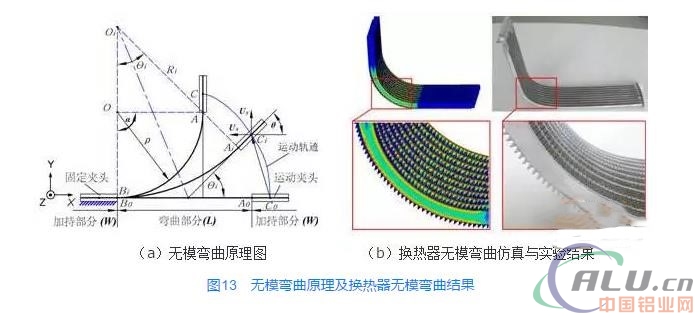
In order to shorten the development cycle and adapt to the design of different heat exchangers, a moldless bending technology came into being. Its principle and bending are shown in Figure 13. The dieless bending mold eliminates the bending die in the traditional bending process and is mainly composed of two clamping dies, one of which is fixed, and the other is bent under the control of a computer to a target shape according to a certain movement trajectory. The dieless bending technology can realize bending process with any bending radius because there is no bending die, which improves the versatility of bending equipment and reduces the cost of trial die. For the heat exchanger, because there is no direct contact between the bending die and the fins, the heat exchanger structure is not limited to this type of assembly as shown in Fig. 10, which suppresses the possibility of unstable collapse of the fins from the source. In order to increase productivity and reduce subsequent assembly operations, it is also possible to stack two heat exchangers together for one bend.
4, summary
Under the background of increasing energy saving and environmental protection requirements and pressure, parallel-flow heat exchangers have become very promising heat exchangers in the air-conditioning and refrigeration industries, and they are developing in the direction of microchannels and enhanced heat transfer heterogeneous structures. This puts higher requirements on the relevant forming and processing technologies. Since the equivalent flat diameter of the flow channel of the porous flat tube is smaller and smaller under the requirement of enhanced heat transfer, the shape and dimensional accuracy of the product are very sensitive to the deformation of the mold. In order to reduce the extrusion force, the possibility of deformation of the mold is reduced. The development of new mold structures has become a new way to increase the level of manufacturing of porous flat tubes. High-efficiency and compact air-conditioning system requires that the heat exchanger needs secondary bending. The degree of deformation of the tube after secondary processing has an important influence on the overall heat transfer performance of the heat exchanger, and the quality of the flat tube after bending deformation is evaluated. It is of great significance to improve the performance of the heat exchanger and the initial structure of the flat tube. In order to reduce development costs and improve productivity, the use of numerical control dieless bending technology can realize flexible manufacturing of heat exchanger bending process, and reduce the chance of forming defects of the workpiece.
Ningbo Alite Lighting Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.alite-tmwt.com